GLAUCOMA
What is glaucoma?
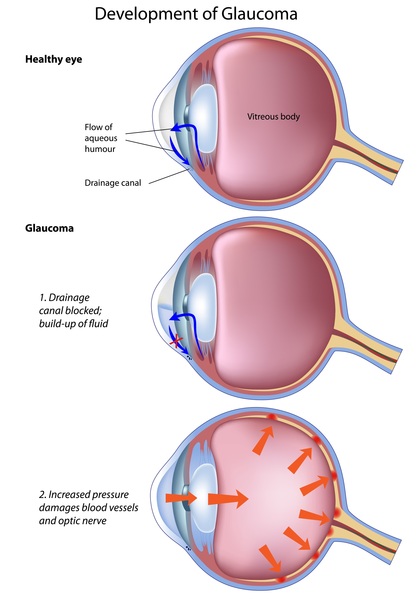
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, causing vision loss and blindness. It is usually caused by increased pressure in the eye.
Who should get tested for glaucoma and when?
Anyone over the age of 40 and people with family history of glaucoma should get tested for glaucoma. The frequency of testing depends on the individual’s risk factors and eye health. An eye doctor can advise on how often to get tested.
What tests are performed to diagnose glaucoma?
Tests for glaucoma usually include:
- Tonometry (measurement of eye pressure)
- Visual field test (detects peripheral vision loss)
- Optic nerve head evaluation (examines the appearance of the optic nerve)
- Pachymetry (measures corneal thickness)
- Gonioscopy (examines the drainage angle of the eye)
These tests are performed by an eye doctor to diagnose and monitor glaucoma.
How is Glaucoma treated?
Glaucoma is treated by lowering the pressure inside the eye and protecting the optic nerve. Treatment options include:
- Medications (eye drops, pills)
- Laser surgery
- Traditional surgery
The type of treatment will depend on the type and severity of the glaucoma, and the individual’s overall health. Early diagnosis and treatment can slow or prevent vision loss.
Why is screening important for glaucoma?
Screening for glaucoma is important because:
- Glaucoma often has no symptoms in its early stages
- Early detection and treatment can slow or prevent vision loss
- Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness, and early detection can preserve sight
Therefore, it’s important to get regular eye exams, especially for those at higher risk for glaucoma. This can help diagnose and treat the condition before significant vision loss occurs